広島大学 先進理工系科学研究科 情報科学プログラム 2021年8月実施 専門科目II 問題2
Author
祭音Myyura
Description
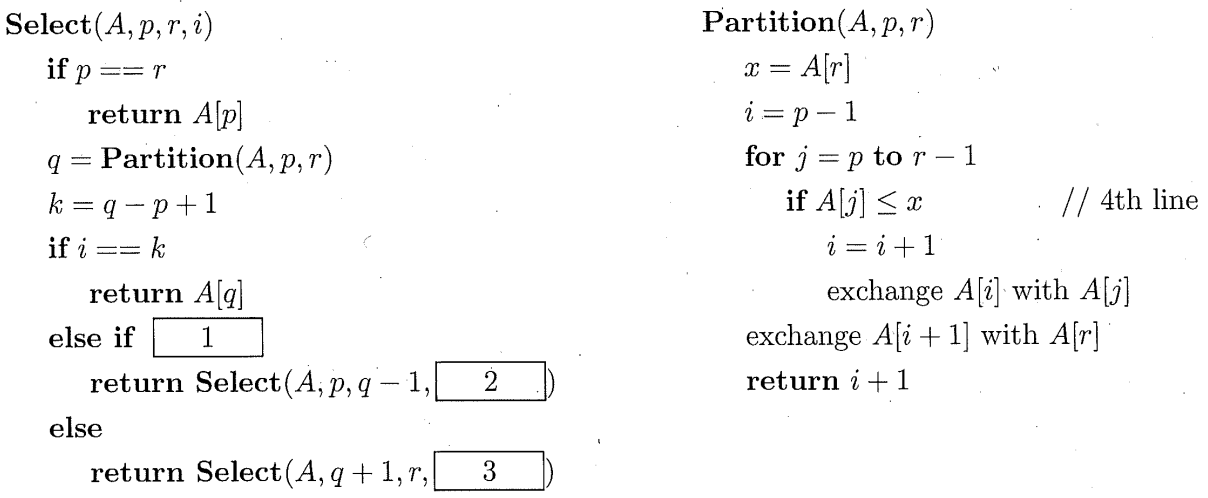
集合の中で \(i\) 番目に小さい要素を探すアルゴリズムを Select(A, p, r, i) に示す。
Select(A, p, r, i) は配列 \(A\) の部分配列 \(A[p]\) から \(A[r]\) のうち \(i\) 番目に小さい要素を返す。
ただし、集合の要素は配列 \(A\) に整列せずに置かれているとする。
また、配列 \(A\) の先頭要素を \(A[1]\) で表す。
(1) 配列 \(A = \{35, 19, 3, 12, 6, 20, 5, 30, 34, 17\}\) に対して Select(A, 1, 10, 3) が返す値を書け。
(2) (1) の配列 \(A\) に対して Select(A, 1, 10, 3) を呼び出すと、Select が再帰的に呼び出される。
最初の呼び出しを含めて、Select の呼出しごとのパラメーター \(A, p, r, i\) の値を書け。
ただし、配列 \(A\) についてはすべての要素を書くこと。
(3) 空欄 \(\boxed{\ \ 1\ \ }\), \(\boxed{\ \ 2\ \ }\), \(\boxed{\ \ 3\ \ }\) を適切に埋める。
(4) 昇順に整列された \(n\) 要素の配列 \(A\) をパラメーターにして Select(A, 1, n, 1) が呼び出されたとき、Partition の 4 行目の比較が行われる回数を数えよ。
(5) \(n\) 個の要素の集合に対する Select の期待計算時間をビッグオー記法で示し、その理由を簡潔に説明せよ。
Select(A, p, r, i) is an algorithm to find the \(i\)-th smallest element in a set.
Select(A, p, r, i) returns the \(i\)-th smallest element in the subarray \(A[p]\) to \(A[r]\) of array \(A\).
We assume that the set is not sorted and resides in array \(A\).
The first element of array \(A\) is represented by \(A[1]\).
(1) For array \(A = \{35, 19, 3, 12, 6, 20, 5, 30, 34, 17\}\), show the return value of Select(A, 1, 10, 3).
(2) When we call Select(A, 1, 10, 3) for array \(A\) shown in (1), Select is called recursively
Describe the values of parameters \(A, p, r, i\) for each recursive call of Select, including the first call. All elements of array \(A\) should be described.
(3) Fill blanks \(\boxed{\ \ 1\ \ }\), \(\boxed{\ \ 2\ \ }\), and \(\boxed{\ \ 3\ \ }\), appropriately.
(4) Count the number of comparisons on the 4th line of Partition, when Select(A, 1, n, 1) is called with sorted array \(A\) of \(n\) elements in ascending order.
(5) Show the expected time complexity of Select for a set of \(n\) elements, using big-\(O\) notation. Explain the reason of the complexity, briefly.
Kai
(1)
\(6\)
(2)
\(A = [35, 19, 3, 12, 6, 20, 5, 30, 34, 17], p = 1, r = 10, i = 3\)
\(A = [3, 12, 6, 5, 17, 20, 19, 30, 34, 35], p = 1, r = 4, i = 3\)
\(A = [3, 5, 6, 12, 17, 20, 19, 30, 34, 35], p = 3, r = 4, i = 1\)
\(A = [3, 5, 6, 12, 17, 20, 19, 30, 34, 35], p = 3, r = 3, i = 1\)
(3)
- blank \(\boxed{\ \ 1\ \ }\): \(i < k\)
- blank \(\boxed{\ \ 2\ \ }\): \(i\)
- blank \(\boxed{\ \ 3\ \ }\): \(i - k\)
(4)
When array \(A\) is in ascending order, the function Partition(A, p, r) will always return \(r\) since all elements in \(A[p \ldots r]\) are less than \(x = A[r]\).
Hence the number of comparisions on the 4th line of Partition is
(5)
Let \(T(n)\) denote the expected time complexity of Select for a set of \(b\) elements.
Then,