広島大学 先進理工系科学研究科 情報科学プログラム 2021年1月実施 専門科目I 問題4
Author
samparker, 祭音Myyura
Description
地点 \(v \sim z\) 電力網を構築することを考える。 図1に示したグラフ \(G\) の各頂点(vertex)は地点 \(v ~ z\) のいずれかに対応し、各辺(edge)はその両端に対応する2地点間に電力線が設置可能であることを示し、各辺に添えられた数字はその費用を示す。 以下の設問に答えよ。
(1) グラフ \(G\) に関して \(0\) または \(1\) を要素とする隣接行列(adjacency matrix)\(A\) とそれに対応するラプラシアン行列(Laplacian matrix)\(L\) を示せ。
(2) グラフ \(G\) のスパニング木(spanning tree)は、各地点を一度だけ通り、かつ、閉路(cycle)のないような連結した電力網に対応する。 そのような異なるスパニング木が何通りあるか示せ。 ただし、根拠も示せ。
(3) 前問(2)のうち、最も費用のかからないスパニング木を見つけてその総費用を示せ。
Suppose we want to lay out an electric power grid to connect locations \(v \sim z\). In Graph \(G\) shown in Figure 1, each vertex corresponds to one of the locations \(v \sim z\), and each edge represents that an electric power line is possible to construct between the locations at the endpoints of the edge, with which the digit indicates its cost. Answer the following questions:
(1) Show the adjacency matrix \(A\) where each element is \(0\) or \(1\) and the corresponding Laplacian matrix \(L\) of Graph \(G\).
(2) A spanning tree of Graph \(G\) can be defined as a connected electric power grid that visits each location exactly once, not forming a cycle. Show how many different spanning trees are possible for Graph \(G\). Also state the reasons for your answer.
(3) Out of the possible spanning trees considered in Question (2) above, find the one with the least total cost and show that total cost.
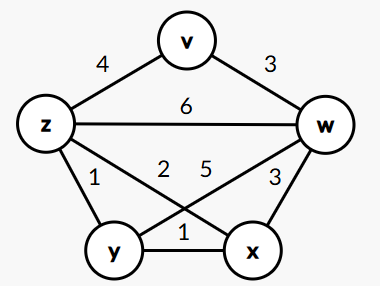
図 1 Figure 1
Kai
(1)
Adjacent matrix
Degree Matrix \(D\)
Laplacian matrix \(L\)
(2)
Kirchhoff's matrix tree theorem: The number of spanning trees in a graph \(G\) is given by \(\text{det}(L_G[i])\), for any \(i\).
Therefore, there are \(40\) different spanning trees in graph \(G\).
(3)
A minimum spanning tree of \(G\) is \(\{zy, yx, xw, wv\}\), whose cost is \(8\).