東京大学 情報理工学系研究科 電子情報学専攻 2024年8月実施 専門 第3問
Author
祭音Myyura
Description
最小全域木(Minimum Spanning Tree, MST)問題とは,
- グラフ
のすべての頂点 を含む. - サイクル(閉路)が存在しない,木の構造である.
- エッジの重みの総和が最小である.
解答にあたっては,以下の仮定を前提とすること.
- ソート関数を使う場合には,長さ
の配列に対して の計算量を仮定すること. - 各頂点がどの集合に属しているかの判定や,2 つの異なる集合の統合操作は,例えば互いに素な集合データ構造(Union–Find)を用いることで定数時間で行えること.
- 優先度付きキューを使用する場合には,ヒープによって実装されたものを使うこと.
以下の問いに答えよ.
(1) 最小全域木問題を解くアルゴリズムの方針とその擬似コードを簡潔に示せ.なお,アルゴリズムは決定的かつ時間計算量が
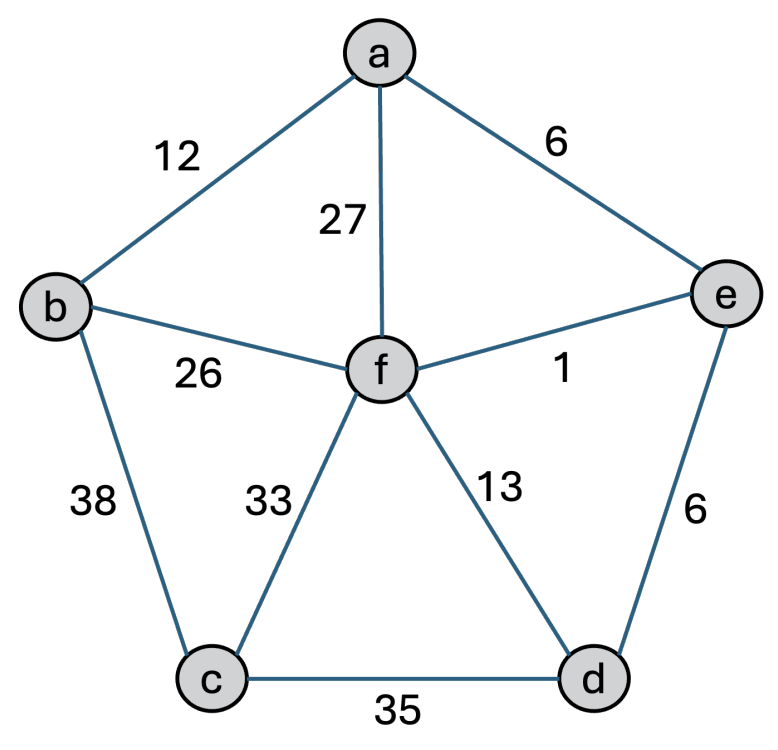
(2) (1) で示したアルゴリズムを用いて 図 のグラフの最小全域木とエッジの重みの総和を示せ.
(3) 全域木の中でエッジの重みの和が 2 番目に小さい全域木(以下,Second MST と呼ぶ)を求めるアルゴリズムの方針とその擬似コードを簡潔に示せ.また,時間計算量を示せ.
(4) (3) で示したアルゴリズムを用いて 図 のグラフの Second MST とエッジの重みの総和を示せ.
Kai
(1)
KruskalMST(G=(V,E), w):
sort edges E by weight ascending # O(|E| log |E|)
UF = UnionFind(|V|)
T = ∅ ; WT = 0
for each (u,v) in E (in ascending weight):
if UF.find(u) != UF.find(v): # O(1)
UF.union(u,v)
T.add((u,v))
WT += w(u,v)
if |T| == |V|-1: break
return T, WT
Total complexity:
(2)
(3)
The second-best minimum spanning tree differs from the MST by exactly one edge substitution. This property is discussed in Introduction to Algorithms (Cormen et al.), Problem 23-1, and the proof can be found in various publicly available solution notes and online discussions of CLRS exercises.
Using Kruskal's algorithm
We can use Kruskal's algorithm to find the MST first, and then just try to remove a single edge from it and replace it with another.
- Sort all edges of the graph in non-decreasing order of their weights, which requires
. - Apply Kruskal’s algorithm to the sorted edge list to obtain an initial minimum spanning tree
, Since edge sorting has already been performed, this step requires time. - For each edge
(there are such edges), temporarily remove it from the edge set so that it cannot be selected. Using the remaining edges, apply Kruskal’s algorithm again to construct a new spanning tree (if possible). Each such computation can be performed in time. - Among all feasible spanning trees
obtained above, select the one whose total weight satisfies and , where enotes the total weight of the initial MST .
The overall time complexity will be
Based on Lowest Common Ancestor (LCA) problem
Please refer to stackoverflow, 22109647, faster-second-best-mst-algorithm, the time complexity is