東京大学 情報理工学系研究科 創造情報学専攻 2018年8月実施 筆記試験 第1問
Author
Description
Pixel という型で表現し、その輝度は p.brightness と表現する。
画像は、Pixel の配列 P として与えられる。擬似コード内では、基本的なデータ構造を適宜利用してよい。
計算量については、
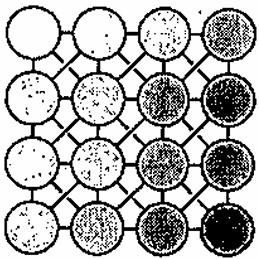
(1) 黒い背景に白い物体がいくつか写っているとする(下図参照)。 そのうちの1つの物体の面積を求める方法として、以下のような方法が考えられる。
「ある閾値に対して、それよりも明るい点のみを残し、それ以外の点を考慮からはずす。残っている点から一つ選び、その点を含む連結領域の大きさ(点の数)を計算する。」
この計算を再帰呼び出しによって行うアルゴリズムを 20 行以内の擬似コードで示し、その計算量を

(2) 以下のような方法で、白い背景の画像に写っている黒い曲線を抽出することを考える(下図参照)。自己交差はないものとする。
「両端の
この計算を効率よく行うアルゴリズムを 20 行以内の擬似コードで示し、その計算量を

(3) 画像を点列で左右に分割する方法として(下図参照)、以下のような方法が考えられる。
「画像の上端と下端を結び、各行につき 1 点を経由するような連結された点列を考える。そのような点列のうち、点の明るさの合計が最小になるような点列を求める。」
この計算を効率よく行うアルゴリズムを 20 行以内の擬似コードで示し、その計算量を

(4) 画像をぼかす方法として、以下のような処理が考えられる。
「各内部点(近傍を 8 つ持つ点)について、その 8 近傍点の輝度の平均値を計算する。すべての内部点についてこの平均値を計算した後、すべての内部点の輝度を対応する平均値へと同時に変更する。」
ここで、内部点の元の輝度を並べたベクトルを x、変更後の輝度を 1 列に並べたベクトルを x'、外部点(画像中の点のうち、内部点以外の点)の輝度を並べたベクトルを b として、x, x', b の関係を行列を使って表現しなさい。
適切に行列を定義して、x, x', b の関係式を示せ。
(5) (4) における処理を画像に対して無限回適用すると、画像の輝度 x は
Description (English)
Consider a 256-level 2-dimensional gray-scale image with

(1) Assume that we have multiple white objects in a black background as shown on the right. We consider the method of computing the area of one of the white objects as follows.
"We keep points that are brighter than a given threshold and ignore the rest. We then pick a point from the remaining points and compute the size (number of points) of the connected region containing the point."
Give a pseudo-code (equal or less than 20 lines) of an algorithm that executes the computation using recursion and answer its computational complexity using the big-

(2) We consider the problem of detecting a black curve in a white background (as shown on the right) as follows. Assume that there is no self-intersection.
"Consider a connected point sequence that connects two end points (assume that the end points are given). Among such point sequences, we would like to obtain one with the minimum total brightness (sum of point brightness on a sequence) along this sequence."
Give a pseudo-code (equal or less than 20 lines) of an algorithm that executes the computation efficiently and answer its computational complexity using the big-

(3) We consider the problem of dividing an image into left and right at a point sequence (as shown on the right) as follows.
"Consider a point sequence that connects top and bottom of the image, containing a single point in each row. Among such point sequences, we would like to obtain one with the minimum total brightness."
Give a pseudo-code (equal or less than 20 lines) of an algorithm that executes the computation efficiently and answer its computational complexity using the big-

(4) We blur an image by applying the following operation to the image.
"For each internal point (a point that has 8 neighbors), we compute the average of brightness of its 8 neighbors. Once we have computed this average for all the internal points, we update the brightness of each internal point to the corresponding average."
We define three vector representations,
(5) The brightness of the points
Kai
(1)
Grayscale image, represented by P of Pixels. Each pixel p has p.brightness which is a 256-level value.
Algorithm:
Given a group of points G and a given point p=(i,j) we will check on a copy of the points:
- If the current pixel does not exists in the remaining group we return 0.
- Else, we mark it as visited (change the brightness to 0 for example).
- We will call on all neighbores we find recursively with the modified data (the visited point).
- we will add the number found by the recursion to 1 and continue.
Since it the part is strongly connected we will find all the number of pixels in the group.
P: a copy of the array, by referencepi,pj: index i and j of the current pixelth: the threshold
function size_of_area(P, pi, pj, th):
if P[i,j].brightness < th:
return 0
P[i,j].brightness = 0
val = 1
i = -1
while i < 2
j = -1
while j < 2
if i == 0 and j == 0:
continue
val = val + size_of_area(P, pi+i, pj+j, th)
j = j + 1
i = i + 1
return val
Time complexity would be
(2)
Using Single Source Shortest Path algorithm we will find the weight of the shortesdt path from p1 to p2. Given the assumptions all weights are non-negative thus we can use the Dijkstra algorithm.
Let us define:
PQ: minimum pariority queue of(key, value)where key is the pixel and value is the shortest path to it.W: weight array for all pixels.
function lowest_sum_of_connection(P, p1, p2):
PQ = [(p1,p1.brightness)]
W = [inf] // array with weight infinity
prior = [null] // array with prior pixels of the shortest path
while PQ not empty:
p0 = PQ.pop() // lowest value (key,value) pair
i = -1
while i < 2:
j = -1:
while j < 2:
if i == 0 and j == 0:
continue
if p0.j+j < n or p0.i+i < n:
continue
if W[p0.i+i,p0.j+j] > p0.value + P[p0.i+i,p0.j+j].brightness:
PQ.insert((P[p0.i+i,p0.j+j], p0.value + P[p0.i+i,p0.j+j].brightness))
prior[p0.i+i,p0.j+j] = p0
j = j + 1
i = i + 1
if p0 == p1:
return W[p1.i, p1.j]
Time complexity is
(3)
Similarly to (2) we the SSSP algorithm, but we will create an new start pixel s which will have brightless set to 0 and is connected with all pixels in the first row.
function best_vertical_partition(P):
PQ = [(s,0])]
W = [inf] // array with weight infinity
prior = [null] // array with prior pixels of the shortest path
i = 0
while i < n:
PQ.insert((P[0,i],P[0,i].brightness))
while PQ not empty:
p0 = PQ.pop() // lowest value (key,value) pair
i = 1
j = -1
while j < 2:
if p0.j+j < n or p0.i+i < n:
continue
if W[p0.i+i,p0.j+j] > p0.value + P[p0.i+i,p0.j+j].brightness:
PQ.insert((P[p0.i+i,p0.j+j], p0.value + P[p0.i+i,p0.j+j].brightness))
prior[p0.i+i,p0.j+j] = p0
j = j + 1
best_p = min(P[n,j]) // for 0 <= j < n
return path_from_prior(prior, best_p)
Time complexity is as before
(4)
Note: I truly am not sure I understood this question correctly, the definitions are not clear and something is off so I don't know how good is my solution.
Assuming an image such as the internal points (blue) are all pixels in range
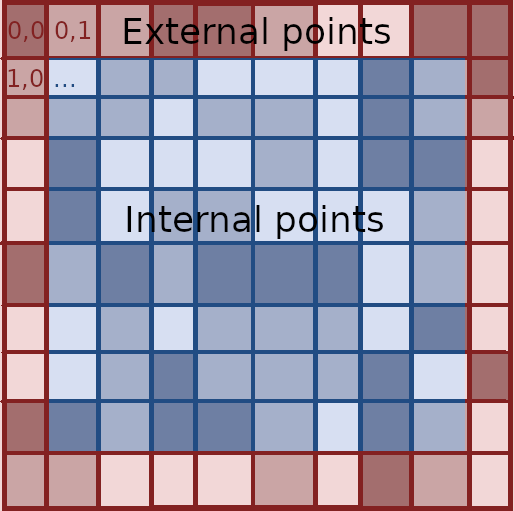
We define
is a matrix of dimension which every row defines which values from will participate in the value for is a matrix of dimension where each row defines which elements from will participate in
(5)
When the method in (4) is repeated, since the values of zero the values of