広島大学 先進理工系科学研究科 情報科学プログラム 2019年8月実施 専門科目II 問題2
Author
samparker, 祭音Myyura
Description
子の数に制約のない根付き木を
(1) 根付き木の節点の数を
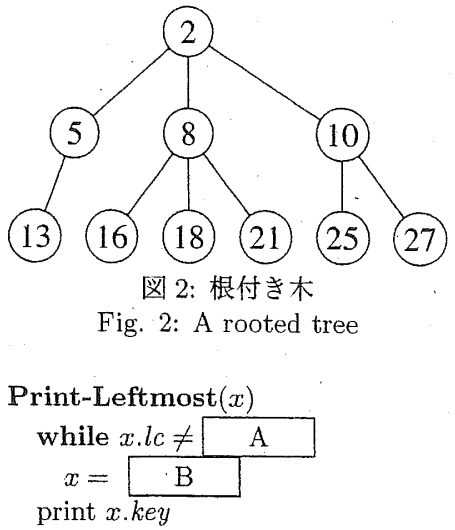
(2) 図 2 の根付き木を、左子・右兄弟表現の 2 分木で表せ。ポインタ
(3) 根付き木の根
(4) 根付き木の根
(5) (4) の手続き Tree-Walk(
There is the left-child, right-sibling representation that uses a binary tree to represent a rooted tree with arbitrary number of children. Each vertex
(1) We assume that a rooted tree has
(2) Draw a binary tree of the left-child, right-sibling representation, to represent a rooted tree shown in Fig. 2. The pointer
(3) The pseudo code Print-Leftmost(
(4) Write a pseudo code of the procedure Tree-Walk(
(5) Show the execution time of Tree-Walk(

Kai
(1)
(2)
2
/
5
/ \
13 8
/ \
16 10
\ /
18 25
\ \
21 27
(3)
(4)
Tree-Walk(x)
if (x != null) then
print(x.key)
Tree-Walk(x.lc)
Tree-Walk(x.rs)